by Enrico | Jun 2, 2024 | herpetology, Lab projects, scientific articles
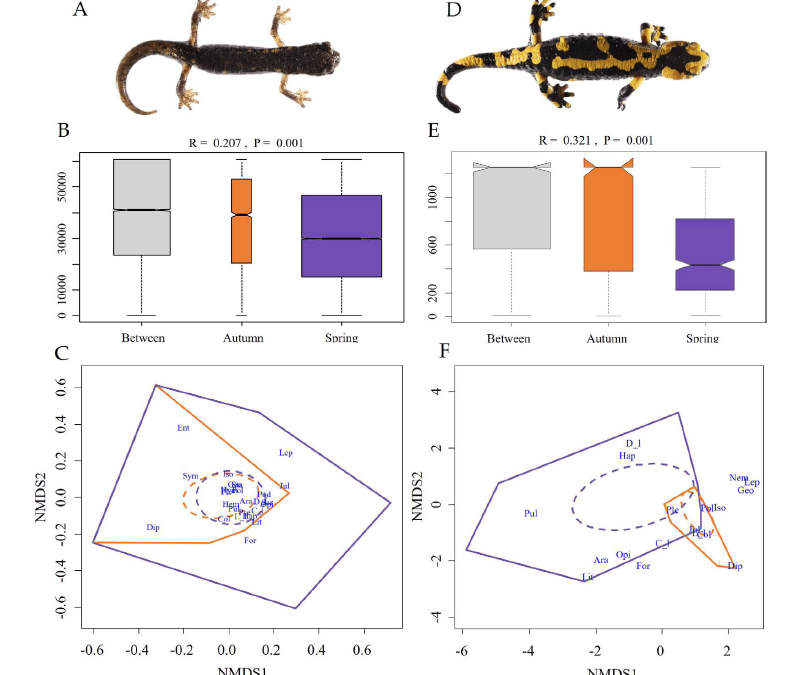
In this article we further studied the trophic niche of two sympatric salamanders: the Fire salamander Salamandra salamandra and the Italian cave salamander Speleomantes italicus. We here collected data on the autumnal diet and, besides comparing that of the two species, for each species we also evaluated seasonal divergences.
Title: Variability of Seasonal Trophic Niche in Two Sympatric Salamanders: Italian Cave Salamanders and Fire Salamanders
Authors: Fabio Cianferoni, Milos Di Gregorio, Claudia Corti, Enrico Lunghi
Journal: Herpetologica
Link to the article Variability of Seasonal Trophic Niche in Two Sympatric Salamanders: Italian Cave Salamanders and Fire Salamanders

by Enrico | Apr 21, 2024 | herpetology, scientific articles, Subterranean biology
In this article we assessed the consistency of individual diet specialization of three populations of Speleomantes ambrosii throughout a period of three years. We found evidence of significant variation of the proportion of specialized individuals between different seasons, and between different years when considering the same season.
Title: Yearly variation in individual diet specialization: Evidence from cave salamanders
Authors: Enrico Lunghi, Gentile Francesco Ficetola, Raoul Manenti, Giorgio Mancinelli
Journal: Global Ecology and Conservation
Link to the article Yearly variation in individual diet specialization: Evidence from cave salamanders
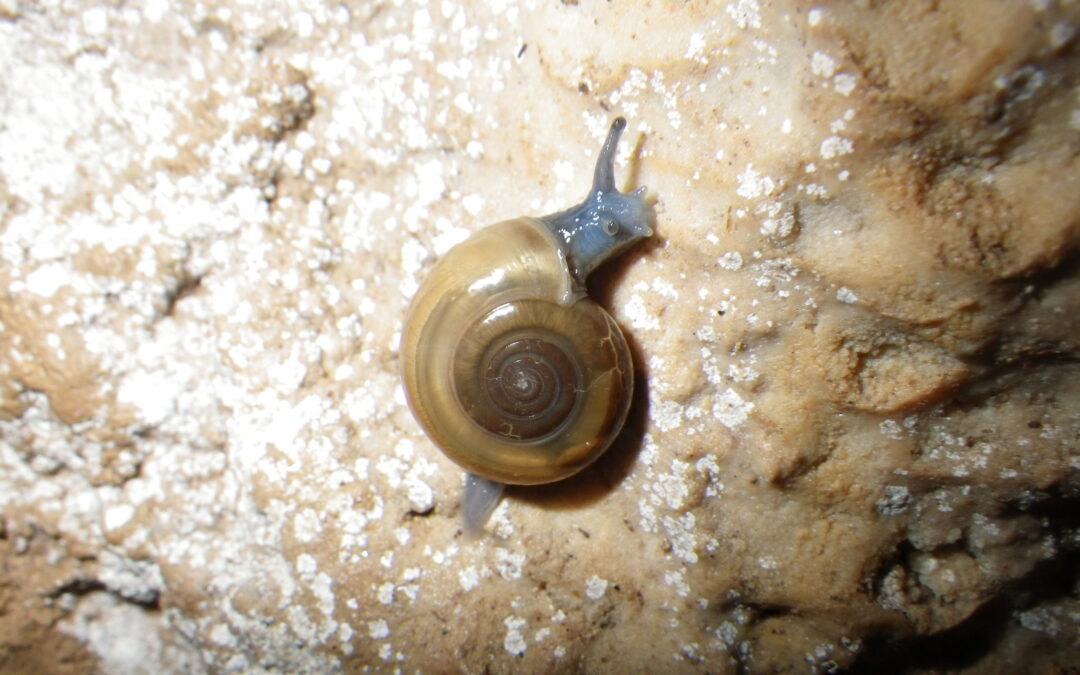

by Enrico | Mar 19, 2024 | scientific articles, Subterranean biology
In this article we analyzed the abundance of three facultative cave species inhabiting the transition zone between surface environment and deep cave areas. Speciefically, we examined the abundance of two spiders and one snail, identifying which are the environmental and biological factors affecting the number of observed individuals.
Title: Microclimatic Influences on the Abundance of Three Non-Troglobiont Species
Authors: Luca Coppari, Raoul Manenti, Enrico Lunghi
Journal: Diversity
Link to the article Microclimatic Influences on the Abundance of Three Non-Troglobiont Species
by admin | Feb 28, 2024 | scientific articles, Subterranean biology
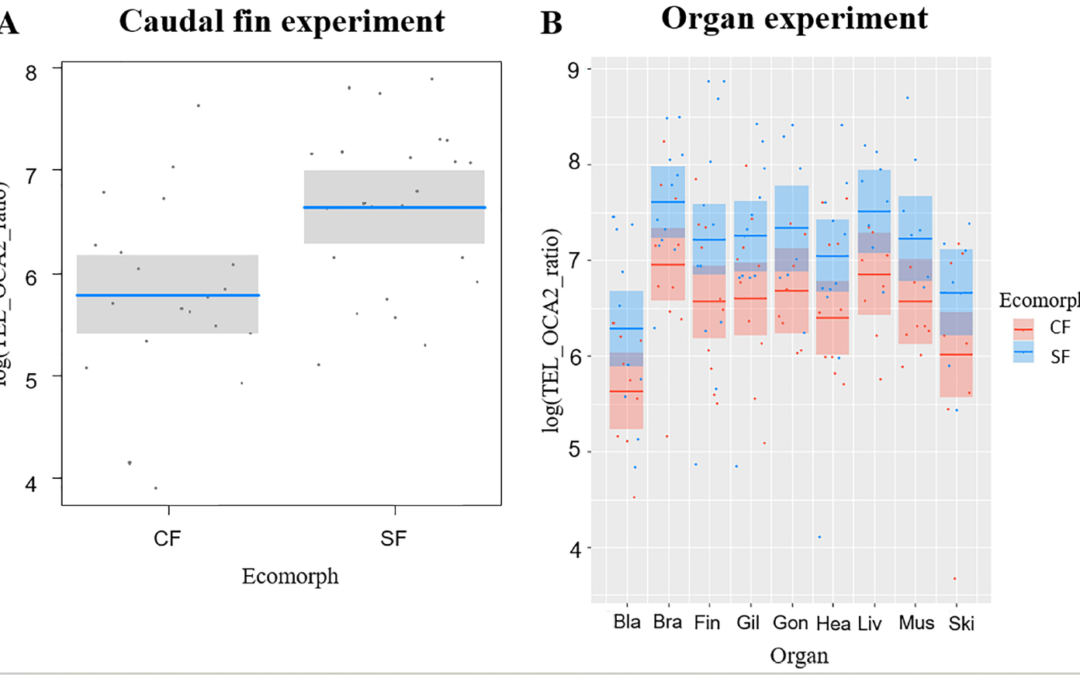
In this article we analyzed the telomere length in both cave and surface form of Astyanax mexicanus. Our results identifies longer telomeres in surface fish compared to cavefish, while no effect of aging was detected within sampled individuals. We hypothesize that telomere lenght likely shortened in cave form as adaptation to the lower stressful environment.
Title: Telomere length and dynamics in Astyanax mexicanus cave and surface morphs
Authors: Enrico Lunghi and Helena Bilandzija
Journal: PeerJ
Link to the article Telomere length and dynamics in Astyanax mexicanus cave and surface morphs
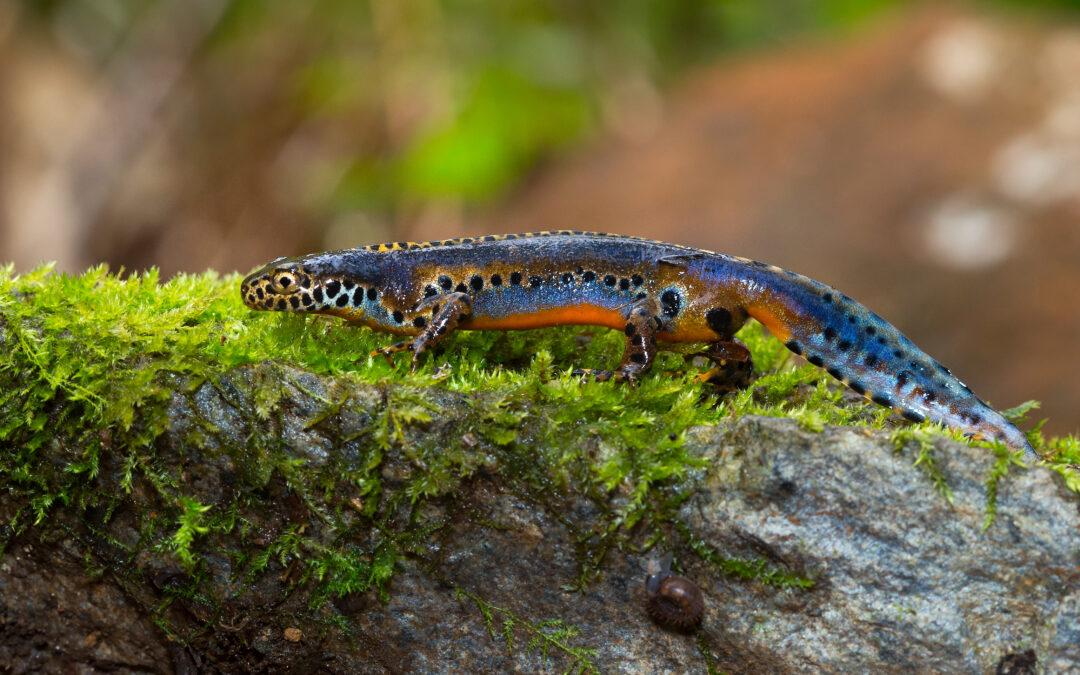

by Enrico | Feb 6, 2024 | scientific articles, Subterranean biology
We are pleased to inform that the collection of articles published in the special issue “Salamanders: Distribution, Diversity, and Conservation” edited by Dr. Lunghi is now available as a book. You can download the pdf for free from the link below.
Title: Salamanders: Distribution, Diversity, and Conservation
Editor: Enrico Lunghi
Journal: Animlas

by Enrico | Jan 29, 2024 | scientific articles, Subterranean biology
We are pleased to inform that the collection of articles published in the research topic “Adaptations to Subterranean Environments” edited by Dr. Lunghi, Prof. Niemiller and Dr. Bilandzija is now available as ebook. You can download the pdf for free from this link.
We collected 13 papers, 8 research articles and 5 reviewes. Below our editorial.
Title: Adaptations to Subterranean Environments
Editors: Enrico Lunghi, Matthew Niemiller, Helena Bilandzija
Journal: Frontiers in Ecology & Evolution
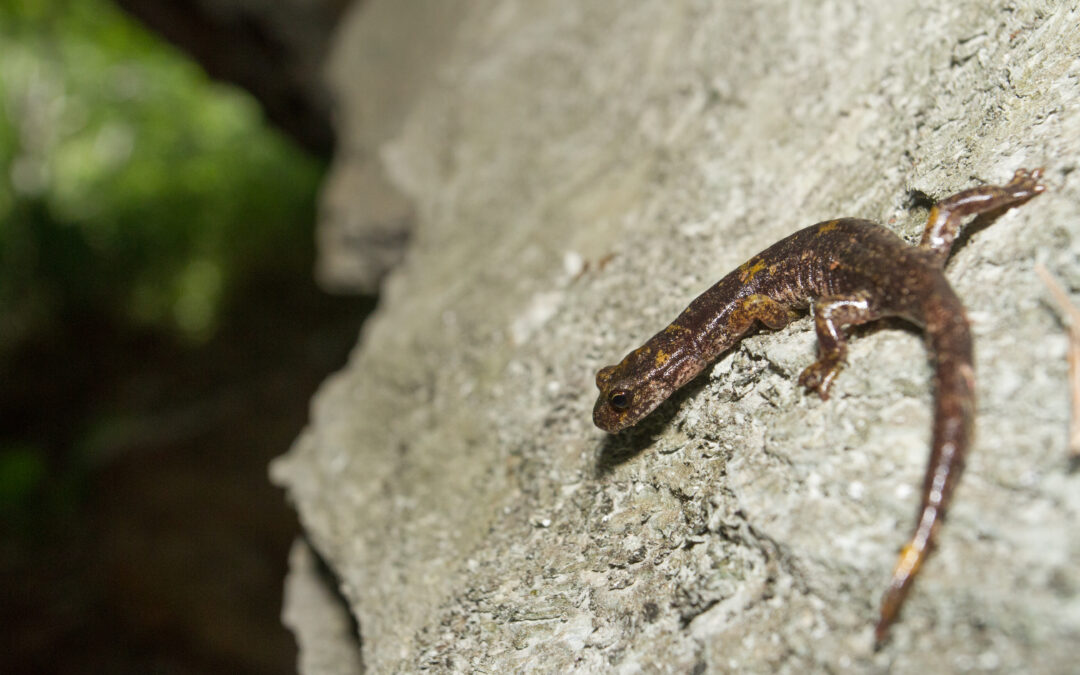

by Enrico | Dec 18, 2023 | scientific articles, Subterranean biology
We are pleased to inform that the collection of articles published in the special issue “Cave Communities: From the Surface Border to the Deep Darkness” edited by Dr. Manenti and Dr. Lunghi is now available as a book. You can download the pdf for free from the link below.
Title: Cave Communities: From the Surface Border to the Deep Darkness
Editors: Raoul Manenti and Enrico Lunghi
Journal: Diversity
by Enrico | Dec 15, 2023 | herpetology, scientific articles, Subterranean biology
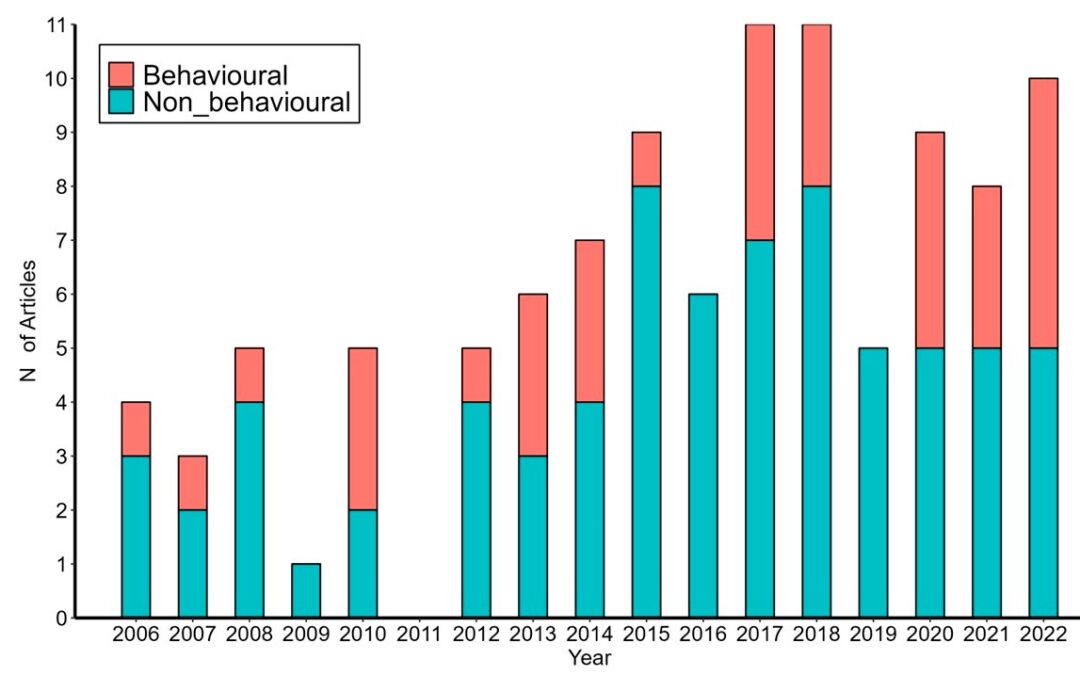
In this article we performed a review aiming to define the state-of-the-art of researches published on the behabviour of Speleomantes cave salamanders, and we provided insights for future researches aiming to fill the current knowledge gap.
Title: Recent Advances in the Behavioral Ecology of European Plethodontid Salamanders
Authors: Andrea Costa , Enrico Lunghi, Giacomo Rosa, Sebastiano Salvidio
Journal: Animals
Link to the article Recent Advances in the Behavioral Ecology of European Plethodontid Salamanders
by Enrico | Oct 31, 2023 | scientific articles, Subterranean biology
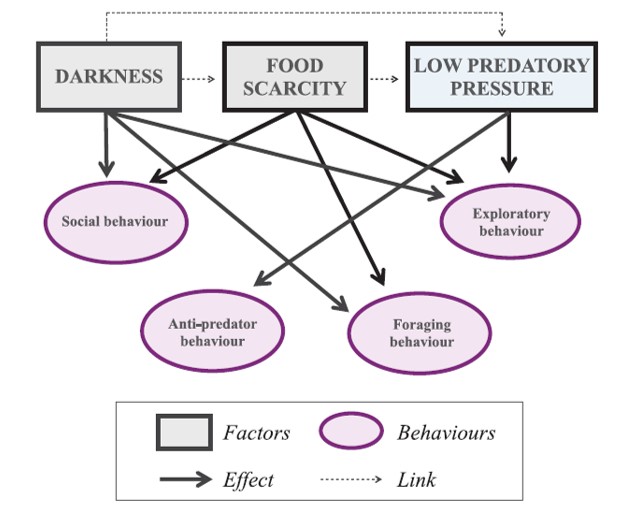
In this article we performed a review of research papers in which experiments or description of specific behavioural trait were performed in cave species. Data was then analysed to assess the convergent evolution of such behavioral traits, and to infer on the role that behavioural adjustments may have during the colonization of subterranean environments.
Title:
Behavioural adjustments enable the colonization of subterranean environments
Authors: Enrico Lunghi , Stefano Mammola, Alejandro Martínez, Thomas Hesselberg
Journal: Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society
Link to the article Behavioural adjustments enable the colonization of subterranean environments
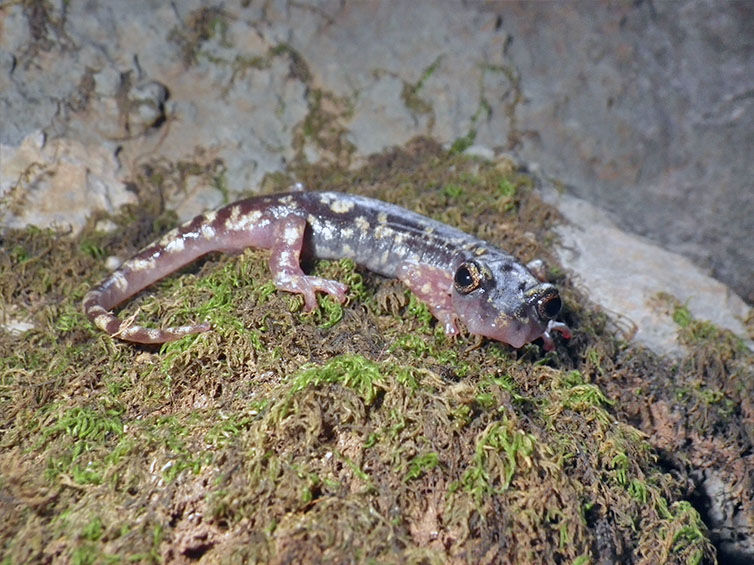

by admin | Sep 1, 2023 | herpetology, scientific articles
In this article we performed a fine-scale analysis of the gut contents obtained from all Speleomantes species, including hybrids. Identifying prey with higher taxonomic resolution and considering their ecology, we were able to infer on potential foraging behaviour of these salamanders, paving the way for future studies to test these new hypotheses.
Title:
Inferring on Speleomantes Foraging Behavior from Gut Contents Examination
Authors: Fabio Cianferoni, Enrico Lunghi
Journal: Animals
Link to the article Inferring on Speleomantes Foraging Behavior from Gut Contents Examination
Special Issue: Predator-Prey Interactions in Amphibians and Reptiles










